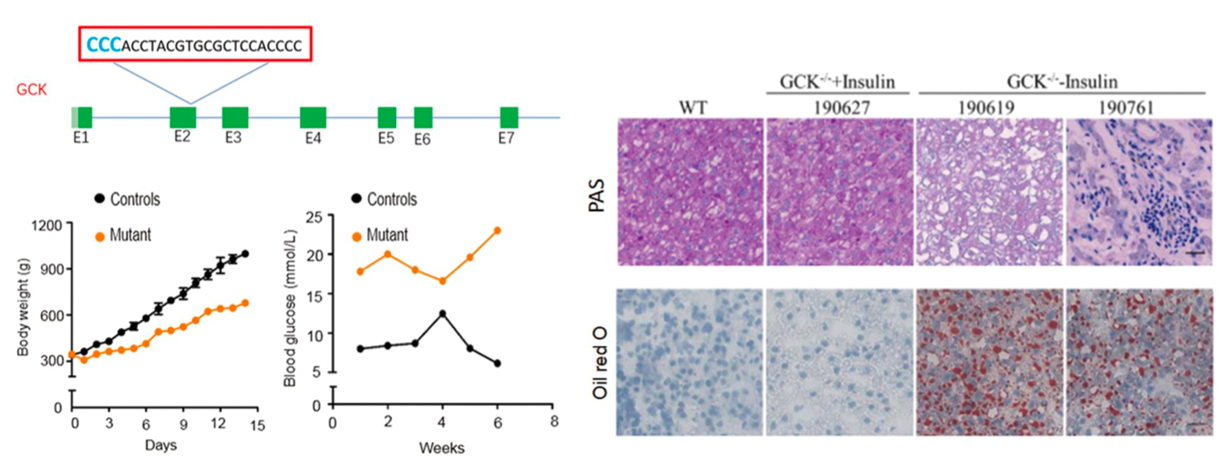
Neonatal diabetes mellitus (NDM) is one of the most unusual and exceptional type of diabetes that occurs in infants before the age of 6 months. Transient neonatal diabetes mellitus (TNDM) and permanent neonatal diabetes mellitus (PNDM) have been identified clinically. Permanent neonatal diabetes is the main type of neonatal diabetes. Compared with temporary neonatal diabetes, its clinical symptoms are more serious and the onset is often in the state of ketoacidosis. In addition, there is no self-remission process after the onset of permanent neonatal diabetes and lifelong treatment is required. PNDM is an autosomal dominant disorder. PNDM in humans can be caused by the homozygous nullification of glucokinase (GCK), which is a key rate-limiting enzyme in glucose metabolism in pancreatic β cells and hepatocytes and is considered as the “glucose sensor” for the regulation of insulin secretion. Here, for the first time, by utilizing a newly developed base-editing technology named BE3 system, we attempted to generate a dog model of PNDM that contained homozygous GCK point mutations.
>
电话:+86 13910991951
email:service@sinogene.com.cn