In the study of cancer-related diseases, although transgenic mice are an effective tool for modelling the mutation dynamics of various cancers, mouse and human cancers are biologically different. Therefore, studies in mouse models often fail to be successfully translated into clinical settings. Only 5% of anticancer drugs developed in preclinical studies based on traditional mouse models demonstrated sufficient efficacy in Phase III testing. In contrast, pigs share many similarities with humans. Cre-dependent Cas9-expressing pigs with primary tumors will provide a new platform for developing novel models of human cancer, eventually facilitating new diagnostic and therapeutic technologies.
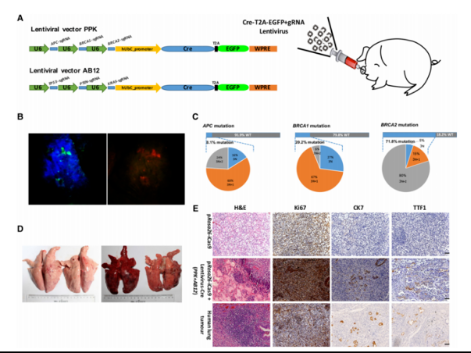
In 2017, using gene editing technology mediated by transcription activator-like effector nuclease (TALEN) and somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT), Lai Liangxue’s research group at the Guangzhou Institute of Biomedicine and Health, Chinese Academy of Sciences, generated the first pig model where the Cre-dependent Cas9-expressing cassette was specifically inserted into the Rosa26 locus. Using this tool model to directly edit the pig’s genome, we are able to streamline the generation of genome-edited pigs for disease modeling.This pig line with Cre-inducible Cas9 expression allows a variety of ex vivo genomeediting in fibroblast cells including single- and multigene modifications, chromosome rearrangements, and efficient in vivo genetic modifications.Through lentiviral infection, mutations in five tumor suppressor genes (TP53, PTEN, APC, BRCA 1 and BRCA 2) and a proto-oncogene (KRAS) related to pig lung cancer were successfully induced in vivo, thereby successfully establishing a large animal model of primary lung cancer using gene-editing technology.