
电话:+86 13910991951
email:service@sinogene.com.cn


● Model types: Subcutaneous, Orthotopic, Whole body or Metastatic models
○ Subcutaneous models:CDX model and Syngeneic model. Detection of tumor growth by vernier calipers
○ Orthotopic models: Liver, Lung, Brain, Breast, Pancreas, Prostate (castrated/non-castrated) in situ. Detection of tumor growth by IVIS in vivo imaging
○ Systemic or metastatic models: Evaluation of tumor metastasis ability, hematological tumor and lung metastasis models. Detection of tumor growth through IVIS in vivo imaging
The selection of model species is critical to the successful establishment of animal models. The genetic sequences of rodents and humans have 90% homology, and their anatomical structures are highly similar, making them a better choice for establishing animal models. The experimental period of mice is short and the economic cost is low, so mice are generally chosen as tumor model animals.
Commonly used mouse strains include: BALB/c Nude, CB17 SCID, NOD SCID, NOG, BALB/c, C57BL/6, etc.
Simple operation, short experimental cycle, high modeling success rate, high repeatability, and relatively low experimental cost
For drug target verification, pharmacodynamic evaluation, PK/PD research, safety evaluation of cell gene therapy products (maximum tolerated dose (MTD) analysis) and multi-drug synergistic efficacy evaluation, etc. It is an important preclinical animal model to evaluate immunotherapeutic efficacy of antitumor drugs.
Liver cancer cell line: Huh7 liver in situ HE staining
Lung cancer cell line—LLC lung in situ HE staining
Liver cancer cell line: Huh7 tail vein injection lung metastasis
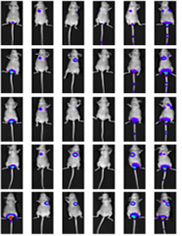
Liver cancer cell line: Huh7 orthotopic inoculation
Kindly fill out this short message and we will contact you in 24hrs.