
电话:+86 13910991951
email:service@sinogene.com.cn

In the 18th century, scientists discovered that removal of the pancreas in dogs led to the development of diabetes. Because of the similarity between canine and human digestive systems, Canadian physician Dr. Banting decided to extract pancreatic material from dogs for diabetes research. In 1921, Banting and Best successfully treated diabetic dogs using pancreatic extracts from experimental dogs (later named insulin), resulting in decreased blood sugar levels in the dogs, indicating its potential to lower blood sugar and treat diabetes. The discovery of insulin represented major scientific breakthrough in the history of diabetes, bringing new hope to diabetes patients.
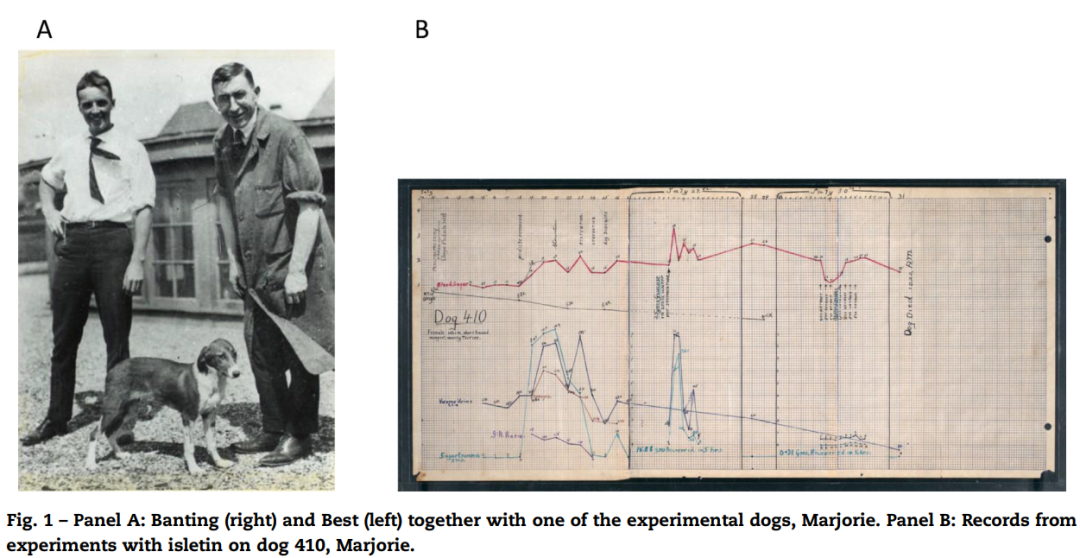
One biological characteristic of dogs as model animal is their well-developed nervous system. As early as the beginning of the 19th century, the renowned Russian physiologist Ivan Petrovich Pavlov used dogs as a model animal to propose the classic theory of conditional reflexes. His experiments also demonstrated the highly developed nervous system of dogs, marking the significant beginnings of using dogs as model animals in scientific research.
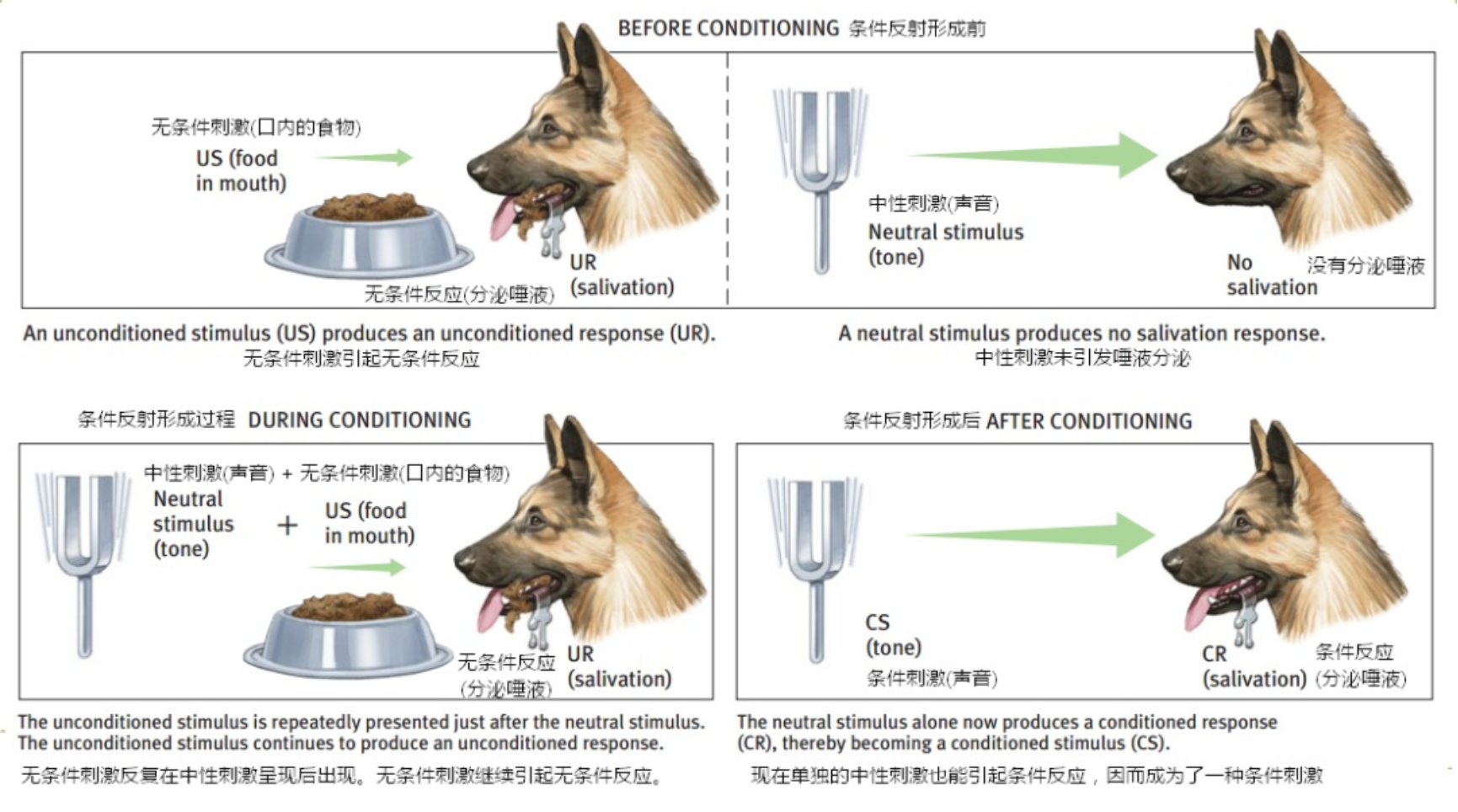
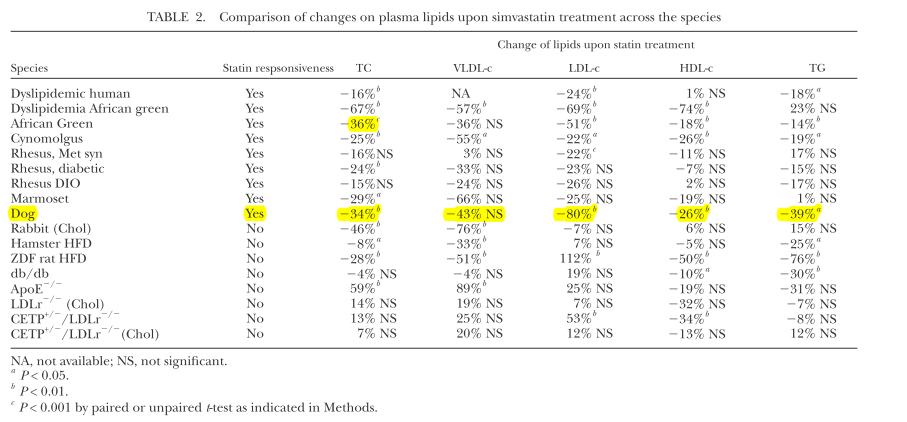
Table 1【1】 Research findings indicate that, from the perspective of lipid metabolism, among all experimental animals, dogs and non-human primates show a significant reduction in lipid levels when treated with statins. Therefore, in terms of lipid pathways, dogs are quite similar to humans.
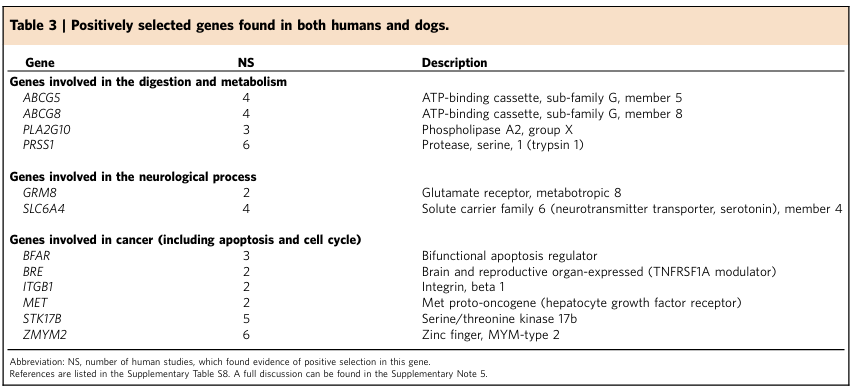
Table 2【2】 By using the whole-genome sequencing technology, we have discovered that over the course of more than 30,000 years of domestication, dogs have developed dietary habits and living environments tend to resemble those of humans. Furthermore, due to long-term convergent evolution, dogs and humans exhibit remarkably similar gene expression in aspects such as digestive metabolism and the nervous system. This genomic convergent evolution illustrates the similar living environments and unique cross-species relationships between the two, providing us with a unique opportunity to study the genetics and evolution of dogs and humans.
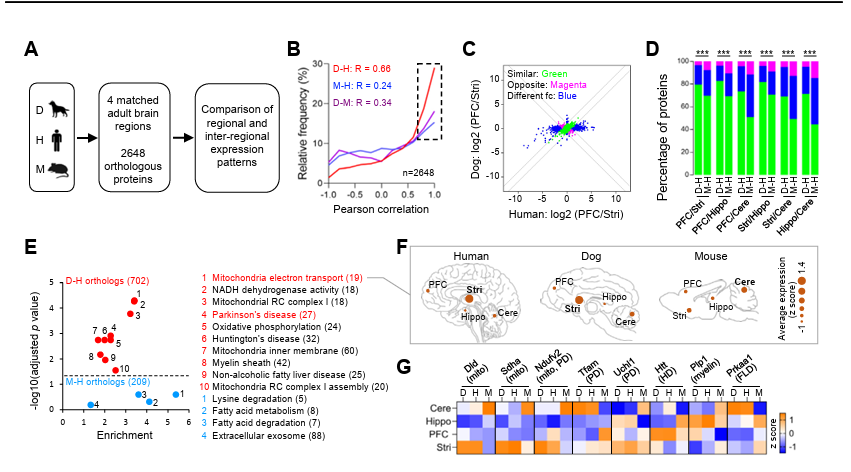
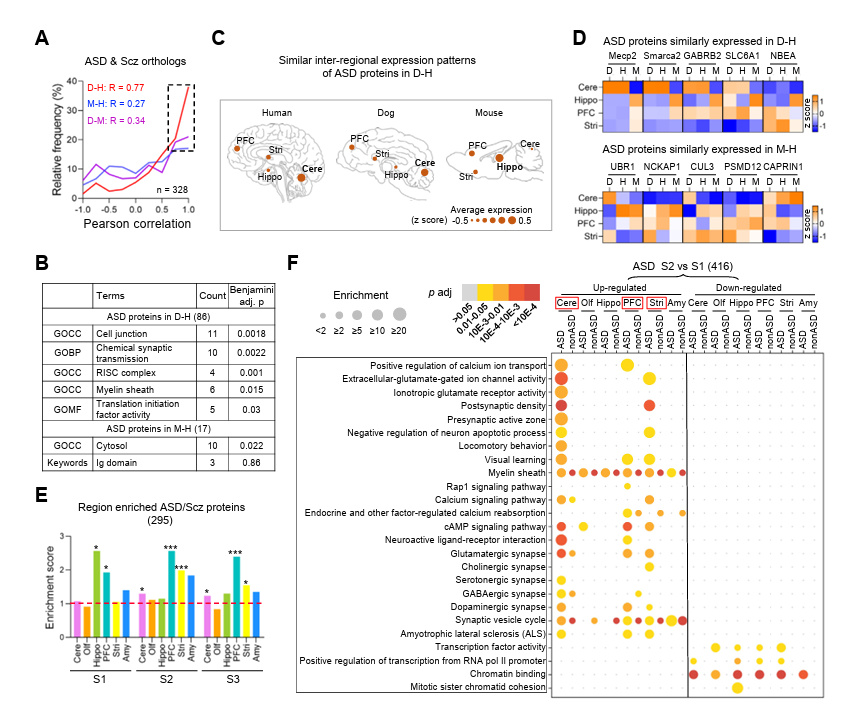
According to the latest research published by Professor Zhang Yongqing from the Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences[3], the results indicate that the homologous protein regional expression patterns in myelin, hippocampus, mitochondria, and brain disease-related pathways between dogs and humans are highly correlated. This similar regional expression pattern provides a theoretical basis for using dogs as a model animal for mechanistic and translational research.

Over the course of more than 30,000 years of domestication, dogs have developed highly advanced social cognitive abilities based on the foundation of the gray wolf. They can interpret human social cues, such as gestures, gazes, and establish strong social bonds with humans. Dogs can understand human social signals by interpreting human language and social body language, provide feedback, which is a relatively unique advantage compared to other species.

In 2015, an article published in Science introduced a research team from Japan that conducted an experiment involving 30 domestic pet owners and their pets. During a 30-minute intimate social interaction, eye contact between the pet owners and their pets was established. Urine samples were collected from both the participants and the dogs before and after the experiment. The study found that eye contact could elevate oxytocin levels in both dogs and humans. Oxytoc plays a role in our social relationships. Therefore, the perspective of social behavioral mechanisms, dogs are also well suited for conducting related behavioral studies.

A research team from Hungary conducted functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) on awake dogs and discovered that in the canine brain, the auditory brain region responsible for perceiving emotions in sounds is nearly identical to that of humans, located in the right temporal lobe. Based on the above characteristics, we believe that dogs are well-suited for the development of disease models in areas such as cardiovascular, neurological, rare diseases, metabolic disorders, etc.
Kindly fill out this short message and we will contact you in 24hrs.